Choose a test user to login and take a site tour.





5 minutes, 33 seconds
-47 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews
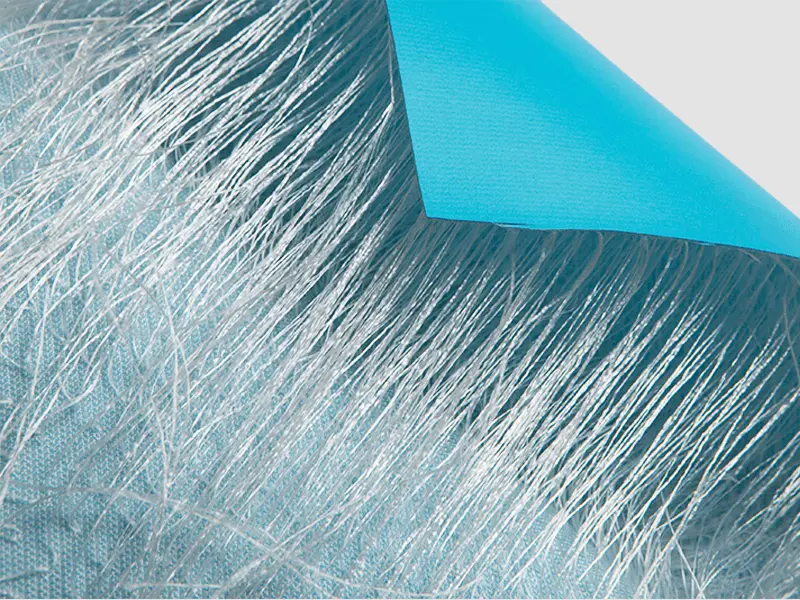
Modern industrial design increasingly depends on lightweight materials that deliver strength, stability, and adaptability across multiple environments. This shift has intensified interest in advanced structural textiles, especially in projects where inflatable systems, modular equipment, and temporary load-bearing components must function with high reliability. Within these innovations, discussions of engineered dual-layer textiles frequently reference Double Wall Fabric as a benchmark for consistent geometry and mechanical efficiency. Shanghai Mingda International Trade Co. actively contributes to this field by offering material variants optimized for durability and precision manufacturing.
The core advantage of this textile lies in its ability to sustain an engineered gap between its two surfaces. This gap is maintained by a dense, uniform network of spacer yarns that form an internal lattice. When the textile is pressurized, these yarns act as miniature columns, transferring forces evenly across the surfaces and preserving the structure’s intended thickness. The result is a flexible yet remarkably stable material capable of supporting significant loads, a characteristic difficult to replicate with single-layer constructions or rigid alternatives.
Material composition significantly influences long-term performance. High-tenacity polyester yarns offer balanced strength and flexibility, making them suitable for demanding operational cycles. Nylon alternatives provide enhanced abrasion resistance for environments that involve friction, impact, or repeated equipment movement. After weaving, the textile’s surfaces are typically coated with specialized polymers—such as PVC or TPU—to create a unified, sealed outer layer. This coating prevents air or fluid loss and enables the textile to withstand extended exposure to moisture, chemicals, or particulate contaminants.
Production relies on advanced weaving technologies designed to maintain precision at both micro and macro levels. Large-format looms equipped with computerized tension control ensure uniform spacer alignment even across ultra-wide fabrics. Once woven, the material undergoes a multistage surface preparation sequence that may include pre-cleaning, corona treatment, and controlled drying. These steps improve adhesion during coating, which is later applied using knife-over-roll, extrusion, or hot-melt systems. High-frequency welding, hot-air bonding, or laser-based seam processes complete the assembly, creating airtight joints capable of enduring repeated deployment cycles.
Applications extend across sectors that rely heavily on portable or rapidly deployable structures. In industrial operations, the textile is used to manufacture inflatable mats that protect equipment from rough terrain or sensitive surfaces. In recreational and fitness industries, it supports products requiring both cushioning and rigidity, including floating docks, sports platforms, and air-supported training devices. Emergency response teams employ the textile in systems that must be transported quickly and deployed under pressure, such as temporary bridges, access pathways, and stabilization cushions. Shanghai Mingda International Trade Co. frequently works with these diverse industries to customize yarn density, coating thickness, and dimensional properties to match operational needs.
Testing plays an essential role in evaluating the textile’s performance and ensuring suitability for high-stress applications. Tensile and shear tests measure how spacer yarns respond to inward and outward forces, ensuring that the internal gap remains consistent under dynamic load. Pressure cycling tests simulate repeated inflation and deflation, verifying that the material resists fatigue over thousands of cycles. Abrasion testing evaluates surface durability when the textile contacts rough substrates, an important requirement for both industrial and recreational applications. Additional environmental tests replicate UV exposure, thermal changes, and high humidity levels to confirm long-term surface integrity.
The versatility of this textile has encouraged research into emerging application areas, including temporary architectural systems, portable medical structures, and lightweight transport modules. Engineers are exploring how multi-layer composite versions could enhance stability while reducing weight even further. Meanwhile, coating specialists are developing new formulations that improve fire resistance, puncture behavior, and chemical stability. These innovations will likely expand the material’s presence across industries that require controlled structural performance without relying on rigid frameworks.
With its combination of engineered geometry, mechanical reliability, and adaptability across extreme conditions, this advanced textile continues to support new approaches to portable structures and technical equipment. To learn more about practical uses and product variations, visit https://www.shanghaimsd.com/news/why-is-double-wall-fabric-an-ideal-choice-for-multiple-applications.html .

Share this page with your family and friends.